Islamic Investment Funds in Islamic shariah investment
Islamic Investment funds have gained popularity over the years, especially among Muslim investors who seek to invest their money in a way that aligns with their religious beliefs. Islamic Investment Funds offer a unique approach to investing that is based on ethical and moral principles.
Do you know what is Islamic Fintech? Read this detailed article on Islamic Fintech.
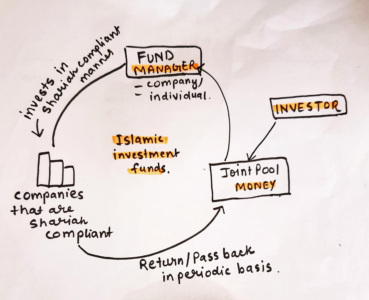
The term “Islamic Investment Fund” means a joint pool wherein the investors contribute their surplus money for the purpose of its investment to earn halal profits in strict conformity with the precepts of Islamic Shari’ah.
Suppose there are investors who have with them surplus liquidity, but these investors do not have the skill and the ability to conduct business, so they would like to invest their surplus with somebody who is a skilled person who knows how to invest the money in strict conformity to shariah principles and give them a return.
Islamic Investment Funds definition
Islamic investment funds, also known as Shariah-compliant or ethical investment funds, are financial vehicles designed for Muslim investors who want to invest their money in accordance with Islamic principles and values. These funds adhere to the guidelines of Islamic finance, which is based on the principles of Shariah law, the moral and ethical code of Islam.
Globally, there are approximately 520 Islamic banks and 1,700 mutual funds that comply with Sharia principles. Between 2012 and 2020, Islamic financial assets grew from $1.7 trillion to $3.1 trillion, and it is expected to further rise to nearly $3.7 trillion by 2024, according to a 2020 report by the Islamic Corporation for the Development of the Private Sector (ICD). Much of this growth is attributed to the economic expansion of Islamic countries, particularly those benefiting from rising oil prices.
Here are the key components and principles that define Islamic investment funds:
- Shariah Compliance: The most fundamental aspect of Islamic investment funds is that they must adhere to the principles of Shariah law. Shariah-compliant investments are guided by Islamic ethics, which prohibit certain financial activities and investments that are considered haram (forbidden). Commonly prohibited activities include involvement in gambling, alcohol, pork, and interest-bearing transactions (riba).
- Prohibition of Riba: The most important principle of Islamic finance is the prohibition of riba, which is often translated as “usury” or “interest.” This means that investments in conventional interest-bearing instruments, such as bonds or fixed-income securities, are not permissible. Instead, Islamic investment funds seek out investment opportunities that do not involve interest, or they use alternative structures compliant with Shariah principles, such as profit-sharing arrangements.
- Asset-Backed Investments: Islamic investment funds typically favor investments in tangible, asset-backed assets. These can include real estate, commodities, equities of Shariah-compliant companies, and other assets with intrinsic value. The underlying assets should be halal (permissible) and not involved in haram activities.
- Avoidance of Speculative and Uncertain Investments (Gharar): Islamic finance discourages investments in speculative and uncertain ventures. This means that gambling-like activities, speculative derivatives, and investments with excessive uncertainty (gharar) are generally avoided.
- Ethical Screening: Besides avoiding haram activities, Islamic investment funds often incorporate ethical screening criteria. These criteria may include environmental and social responsibility, governance practices, and other ethical considerations in their investment decisions.
- Shariah Board Oversight: Islamic investment funds typically have a Shariah board or council composed of Islamic scholars who provide ongoing guidance and supervision to ensure that the fund’s investments remain compliant with Islamic principles.
- Profit and Loss Sharing: Islamic investment funds often employ profit-sharing or loss-sharing mechanisms. This means that investors share in the profits and losses of the underlying investments, aligning their interests with those of the fund manager.
- Transparency: Transparency is a key principle in Islamic finance. Islamic investment funds are required to provide clear and transparent information to their investors regarding the fund’s holdings, activities, and compliance with Shariah principles.
Reasons for the Growth of Islamic Finance
The global growth of the Islamic finance industry from 2021 to 2222 can be attributed to increased bond issuances and continued economic recovery in financial markets. Islamic assets expanded by over 10% in 2020 despite the COVID-19 pandemic.
Islamic banking services are grounded in Islamic beliefs concerning commercial transactions, deriving principles from the Quran. In Islamic banking, all transactions must adhere to Sharia and legal Islamic law, based on Quranic teachings. The rules governing commercial transactions in Islamic banking are referred to as “Fiqh al-Muamalat.”
Are Investment Funds Halal?
Generally, conventional mutual funds are considered haram (forbidden) according to Islamic Sharia principles. However, Islamic investment funds have been specifically designed for Muslim investors, ensuring compliance with halal financial requirements.
What makes Islamic investment funds halal is the nature of the financial assets they invest in, particularly in the stock and securities sectors. It is considered inappropriate, for example, to invest in stocks of companies involved in industries such as alcohol production, gambling, and betting.
Advantages of Islamic Investment Funds
- Diversification and Focus: Islamic investment funds with substantial capital provide the opportunity to diversify investments across multiple financial assets, leading to greater stability in returns and capital protection. This also helps mitigate investment risks.
- Specialized Management: Islamic investment funds usually employ experts and experienced professionals in the field of fund management.
- Liquidity: Investment funds offer high liquidity at relatively low costs for investors who cannot attain it through direct investments.
Conditions of Islamic Investment Funds
The subscribers of the Fund may receive a document certifying their subscription and entitling them to the pro-rata profits actually earned by the Fund. These documents may be called ‘certificates , units’, ‘shares’ or may be given any other name, but their validity in terms of Shari’ah, will always be subject to two basic conditions:
Firstly, instead of a fixed return tied up with their face value, they must carry a pro-rata profit actually earned by the Fund.Therefore, neither the principal nor a rate of profit (tied up with the principal) can be guaranteed. The subscribers must enter into the fund with a clear understanding that the return on their subscription is tied up with the actual profit earned or loss suffered by the Fund.
If the Fund earns huge profits, the return on their subscription will increase to that proportion. However, in case the Fund suffers loss, they will have to share it also, unless the loss is caused by the negligence or mismanagement, in which case the management, and not the Fund, will be liable to compensate it.
Secondly, the amounts so pooled together must be invested in a business acceptable to Shari’ah. It means that not only the channels of investment, but also the terms agreed with them must conform to the Islamic principles.

Also read : Islamic Fintech Industry
Types of investment of Islamic Investment Funds
Keeping these basic requisites in view, the Islamic Investment Funds may accommodate a variety of modes of investment. Some of them are :
- Equity Fund
- Commodity Fund
- Ijarah fund
- Murabaha Fund
- Mixed fund
Equity Fund
Islamic equity funds are one of the latest developments in Islamic financial markets, with their success emerging in the past five years. These funds invest in the shares of companies in a manner that complies with Sharia principles.
Islamic equity funds identify specific companies that are suitable for investment and adhere to Islamic principles, avoiding prohibited activities such as interest-based transactions and the sale of alcoholic beverages. These companies are carefully selected to achieve a balance between returns and risks that align with investors’ preferences.
In an equity fund the amounts are invested in the shares of joint stock companies. The profits are mainly derived through the capital gains by purchasing the shares and selling them when their prices are increased. Profits are also earned through dividends distributed by the relevant companies.
Real estate fund
Another type is real estate fund, which invests in properties that comply with Islamic principles. This includes avoiding investments in properties that generate income from prohibited activities such as alcohol, gambling, and adult entertainment. Real estate funds may also provide investors with exposure to different regions and sectors.
Commodity Fund
Another possible type of Islamic Funds may be a commodity fund. In the fund of this type the subscription amounts are used in purchasing different commodities for the purpose of their resale. The profits generated by the sales are the income of the fund which is distributed pro rata among the subscribers.
Commodity funds rely on purchasing basic commodities with cash and selling them on a deferred basis, typically targeting global commodity markets such as aluminum, copper, and petroleum. The fund’s portfolio is diversified carefully to maximize liquidity and reduce risks in accordance with Islamic principles.These funds may invest directly in physical commodities or through derivatives such as futures contracts. Commodity funds provide investors with exposure to different commodities and may be used as a hedge against inflation.
Sukuk fund
Sukuk funds are another type of Islamic investment fund that invests in sukuk, which are Islamic bonds. Sukuk are structured to comply with Islamic principles and do not pay interest. Instead, they provide investors with a share of the profits generated by the underlying assets. Sukuk funds may invest in different types of sukuk, including government, corporate, and infrastructure sukuk.
Ijarah Fund
Another type of Islamic Fund may be an ijårah fund. Ijårah means leasing. In this fund the subscription amounts are used to purchase assets like real estate, motor vehicles or other equipment for the purpose of leasing them out to their ultimate users. The ownership of these assets remams with the Fund and the rentals are charged from the users. These rentals are the source of income for the fund which is distributed pro rata to the subscribers.
Each subscriber is given a certificate to evidence his proportionate ownership in the leased assets and to ensure his entitlement to the pro rata share in the income. These certificates may preferably be called ‘suknk—-a term recognized in the traditional Islamic jurisprudence.
MURABAHAH FUND
Murabahah is a specific kind of sale where the commodities are sold on a cost-plus basis. This kind of sale has been adopted by the contemporary Islamic banks and financial institutions as a mode of financing. They purchase the commodity for the benefit of their clients, then sell it to them on the basis of deferred payment at an agreed margin of profit added to the cost.
If a fund is created to undertake this kind of sale, it should be a closed-end fund and its units cannot be negotiable in a secondary market. The reason is that in the case of murabahah, as undertaken by the present financial institutions, the commodities are sold to the clients immediately after their purchase from the original supplier, while the price being on deferred payment basis becomes a debt payable by the client.
Therefore, the portfolio of murabahah does not own any tangible assets. It comprises either cash or the receivable debts, Therefore, the units of the fund represent either the money or the receivable.
Salam Funds:
A Salam contract is one in which the delivery of the sold item is deferred while the price is paid in advance. It is considered a permissible contract, provided that certain conditions are met, including specifying the delivery date and location and paying the full price at the time of the contract. Profit can be generated from Salam contracts in investment funds by entering into a parallel Salam contract, where a similar item is sold under the same terms and delivery date. The profit is realized through price differences resulting from market fluctuations and increased value over time.
Read : Murabaha- Islamic shariah compliant Investment
Mixed Fund
Another type of Islamic Fund may be of a nature where the subscription amounts are employed in different types of investments, like equities, leasing, commodities etc. This may be called a Mixed Islamic Fund. In this case if the tangible assets of the Fund are more than 51% while the liquidity and debts are less than 50% the units of the fund may be negotiable. However, if the proportion of liquidity and debts exceeds 50%, its units cannot be traded according to the majority of the contemporary scholars. In this case the Fund must be a closed-end Fund.
Leasing Funds:
Leasing contracts are financial instruments that provide excellent financing options, serving as an alternative to loans and covering the needs of lessees without resorting to interest-based transactions. A lease contract involves the transfer of the right to benefit from an asset capable of generating such benefits, such as housing for a house or transportation for a car. It is a permissible contract, subject to the same conditions as a sales contract for its validity.
Leasing contracts in the United States, for example, are a significant financial activity due to the tax benefits realized when a company chooses leasing over purchasing or borrowing, along with other financial and credit benefits.
Leasing funds depend on owning leased assets, such as equipment, vehicles, aircraft, and sometimes real estate. Income is generated from rental revenues. Leasing funds differ in terms of the type of assets in the fund’s portfolio, with some based on regular leasing contracts, while others use Ijara contracts, which involve a leaseback arrangement. In the latter case, the income generated covers the entire cost of the asset.
Benefits of Investing in Islamic Investment Funds
Investing in Islamic Investment Funds has several benefits that make it an attractive option for investors. One of the most significant advantages is that these funds operate under the principles of Islamic finance, which prohibits investments in industries such as gambling, alcohol, and tobacco. This means that investors can be confident that their money is being used in ethical and socially responsible ways.
Another benefit of investing in Islamic Investment Funds is that they often have a long-term investment horizon, which can lead to more stable returns over time. These funds typically invest in real assets such as property, infrastructure, and commodities, which can provide a hedge against inflation and market volatility.
Islamic Investment Funds also offer diversification benefits, as they invest in a range of different asset classes and sectors. This can help to reduce overall portfolio risk and increase the potential for higher returns.
In addition, many Islamic Investment Funds offer competitive returns compared to conventional investment funds. This is due in part to the fact that these funds are often managed by experienced professionals who are well-versed in the principles of Islamic finance and can identify investment opportunities that align with these principles.
Overall, investing in Islamic Investment Funds can provide investors with a range of benefits, including ethical and socially responsible investing, long-term stability, diversification, and potentially higher returns.
In sha Allah we will discuss all of it in detail.
Read Books on islamic banking and Finance
Excrepts are taken from book : An Introduction to Islamic finance by mufti Taqi uthmani (amazon link)
Discover more from Islam Hashtag
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.




